Duyệt cây trong C
Duyệt cây là một tiến trình để truy cập tất cả các nút của một cây và cũng có thể in các giá trị của các nút này. Bởi vì tất cả các nút được kết nối thông qua các cạnh (hoặc các link), nên chúng ta luôn luôn bắt đầu truy cập từ nút gốc. Do đó, chúng ta không thể truy cập ngẫu nhiên bất kỳ nút nào trong cây. Có ba phương thức mà chúng ta có thể sử dụng để duyệt một cây:
- Duyệt tiền thứ tự (Pre-order Traversal)
- Duyệt trung thứ tự (In-order Traversal)
- Duyệt hậu thứ tự (Post-order Traversal)
Chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu các cách duyệt cây trên qua chương trình C dưới đây:

Cách duyệt cây trong C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data) {
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//kiem tra neu cay la trong
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
}else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//chuyen toi cay con ben trai
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//chen du lieu vao cay con ben trai
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//chuyen toi cay con ben phai
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//chen du lieu vao cay con ben phai
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
struct node* search(int data) {
struct node *current = root;
printf("Truy cap cac phan tu cua cay: ");
while(current->data != data) {
if(current != NULL)
printf("%d ",current->data);
//chuyen toi cay con ben trai
if(current->data > data) {
current = current->leftChild;
}
//chuyen toi cay con ben phai
else {
current = current->rightChild;
}
//khong tim thay
if(current == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
}
return current;
}
void pre_order_traversal(struct node* root) {
if(root != NULL) {
printf("%d ",root->data);
pre_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
pre_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
void inorder_traversal(struct node* root) {
if(root != NULL) {
inorder_traversal(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
inorder_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
void post_order_traversal(struct node* root) {
if(root != NULL) {
post_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
post_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
}
int main() {
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
i = 31;
struct node * temp = search(i);
if(temp != NULL) {
printf("[%d] Da tim thay phan tu.", temp->data);
printf("\n");
}else {
printf("[ x ] Khong tim thay phan tu (%d).\n", i);
}
i = 15;
temp = search(i);
if(temp != NULL) {
printf("[%d] Da tim thay phan tu.", temp->data);
printf("\n");
}else {
printf("[ x ] Khong tim thay phan tu (%d).\n", i);
}
printf("\nCach duyet tien thu tu: ");
pre_order_traversal(root);
printf("\nCach duyet trung thu tu: ");
inorder_traversal(root);
printf("\nCach duyet hau thu tu: ");
post_order_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
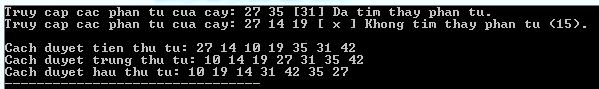
Kết quả
Biên dịch và chạy chương trình C trên sẽ cho kết quả:
Đã có app VietJack trên điện thoại, giải bài tập SGK, SBT Soạn văn, Văn mẫu, Thi online, Bài giảng....miễn phí. Tải ngay ứng dụng trên Android và iOS.
Theo dõi chúng tôi miễn phí trên mạng xã hội facebook và youtube:Follow fanpage của team https://www.facebook.com/vietjackteam/ hoặc facebook cá nhân Nguyễn Thanh Tuyền https://www.facebook.com/tuyen.vietjack để tiếp tục theo dõi các loạt bài mới nhất về Java,C,C++,Javascript,HTML,Python,Database,Mobile.... mới nhất của chúng tôi.
Bài học Cấu trúc dữ liệu và giải thuật phổ biến tại vietjack.com:
- Giải thuật tiệm cận - Asymptotic Algorithms
- Cấu trúc dữ liệu mảng (Array)
- Danh sách liên kết - Linked List
- Cấu trúc dữ liệu ngăn xếp - Stack
- Cấu trúc dữ liệu hàng đợi - Queue
- Tìm kiếm tuyến tính - Linear Search
- Tìm kiếm nhị phân - Binary Search
- Sắp xếp nổi bọt - Bubble Sort
- Sắp xếp chèn - Insertion Sort




 Giải bài tập SGK & SBT
Giải bài tập SGK & SBT
 Tài liệu giáo viên
Tài liệu giáo viên
 Sách
Sách
 Khóa học
Khóa học
 Thi online
Thi online
 Hỏi đáp
Hỏi đáp

